1. What route would have the lowest administrative distance?
a directly connected network*
a static route
a route received through the EIGRP routing protocol
a route received through the OSPF routing protocol
2. Refer to the exhibit.
What command would be used to configure a static route on R1 so that traffic from both LANs can reach the 2001:db8:1:4::/64 remote network?
ipv6 route ::/0 serial0/0/0
ipv6 route 2001:db8:1:4::/64 2001:db8:1:3::1
ipv6 route 2001:db8:1:4::/64 2001:db8:1:3::2*
ipv6 route 2001:db8:1::/65 2001:db8:1:3::1
3. What is a characteristic of the distribution layer in the three layer hierarchical model?
acts as the backbone for the network, aggregating and distributing network traffic throughout the campus
provides access to the rest of the network through switching, routing, and network access policies*
distributes access to end users
represents the network edge
4. Which three statements are generally considered to be best practices in the placement of ACLs? (Choose three.)
Place standard ACLs close to the source IP address of the traffic.
Place extended ACLs close to the destination IP address of the traffic.
Filter unwanted traffic before it travels onto a low-bandwidth link.*
Place extended ACLs close to the source IP address of the traffic.*
Place standard ACLs close to the destination IP address of the traffic.*
For every inbound ACL placed on an interface, there should be a matching outbound ACL.
5. Refer to the exhibit.
How is a frame sent from PCA forwarded to PCC if the MAC address table on switch SW1 is empty?
SW1 floods the frame on all ports on the switch, excluding the interconnected port to switch SW2 and the port through which the frame entered the switch.
SW1 floods the frame on all ports on SW1, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.*
SW1 forwards the frame directly to SW2. SW2 floods the frame to all ports connected to SW2, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
SW1 drops the frame because it does not know the destination MAC address.
6. Which address prefix range is reserved for IPv4 multicast?
240.0.0.0 – 254.255.255.255
224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255*
169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255
127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255
7. Which statement describes a difference between the operation of inbound and outbound ACLs?
In contrast to outbound ALCs, inbound ACLs can be used to filter packets with multiple criteria.
Inbound ACLs can be used in both routers and switches but outbound ACLs can be used only on routers.
Inbound ACLs are processed before the packets are routed while outbound ACLs are processed after the routing is completed.*
On a network interface, more than one inbound ACL can be configured but only one outbound ACL can be configured.
8. What are three primary benefits of using VLANs? (Choose three.)
security*
a reduction in the number of trunk links
cost reduction*
end user satisfaction
improved IT staff efficiency*
no required configuration
9. What routing table entry has a next hop address associated with a destination network?
directly-connected routes
local routes
remote routes*
C and L source routes
10. Which type of inter-VLAN communication design requires the configuration of multiple subinterfaces?
router on a stick*
routing via a multilayer switch
routing for the management VLAN
legacy inter-VLAN routing
11. Which two devices allow hosts on different VLANs to communicate with each other? (Choose two.)
Layer 2 switch
Layer 3 switch*
hub
repeater
router*
12. Which two statements correctly describe a router memory type and its contents? (Choose two.)
ROM is nonvolatile and stores the running IOS.
FLASH is nonvolatile and contains a limited portion of the IOS.
RAM is volatile and stores the IP routing table.*
NVRAM is nonvolatile and stores a full version of the IOS.
ROM is nonvolatile and contains basic diagnostic software.*
13. Refer to the exhibit.
In what switch mode should port G0/1 be assigned if Cisco best practices are being used?
access
trunk*
native
auto
14. Why does a Layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP address and subnet mask?
to identify the broadcast address of the destination network
to identify the host address of the destination host
to identify faulty frames
to identify the network address of the destination network*
15. Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
FEC0::/10
FDEE::/7
FE80::/10*
FF00::/8
16. What are three parts of an IPv6 global unicast address? (Choose three.)
an interface ID that is used to identify the local network for a particular host
a global routing prefix that is used to identify the network portion of the address that has been provided by an ISP*
a subnet ID that is used to identify networks inside of the local enterprise site*
a global routing prefix that is used to identify the portion of the network address provided by a local administrator
an interface ID that is used to identify the local host on the network*
17. An IPv6 enabled device sends a data packet with the destination address of FF02::2. What is the target of this packet?
all IPv6 enabled devices across the network
all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link
all IPv6 DHCP servers
all IPv6 configured routers on the local link*
18. A router is configured to participate in multiple routing protocol: RIP, EIGRP, and OSPF. The router must send a packet to network 192.168.14.0. Which route will be used to forward the traffic?
a 192.168.14.0/26 route that is learned via RIP*
a 192.168.14.0/24 route that is learned via EIGRP
a 192.168.14.0/25 route that is learned via OSPF
a 192.168.14.0/25 route that is learned via RIP
19. Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
192.168.1.64/26*
192.168.1.32/27
192.168.1.32/28
192.168.1.64/29
20. What does the IP address 192.168.1.15/29 represent?
subnetwork address
multicast address
unicast address
broadcast address*
21. Refer to the exhibit.
A network administrator is implementing the stateless DHCPv6 operation for the company. Clients are configuring IPv6 addresses as expected. However, the clients are not getting the DNS server address and the domain name information configured in the DHCP pool. What could be the cause of the problem?
The GigabitEthernet interface is not activated.
The router is configured for SLAAC operation.*
The DNS server address is not on the same network as the clients are on.
The clients cannot communicate with the DHCPv6 server, evidenced by the number of active clients being 0.
22. An organization is assigned an IPv6 address block of 2001:db8:0:ca00::/56. How many subnets can be created without using bits in the interface ID space?
256*
512
1024
4096
23. Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all targets are used.)
24. Match the DHCP message types to the order of the DHCPv4 process. (Not all options are used.)
25. Refer to the exhibit. Match the network with the correct IP address and prefix that will satisfy the usable host addressing requirements for each network. (Not all options are used.)
26. What is the term that is used for the area of a network that is affected when a device or network service experiences problems?
failure domain*
collision domain
broadcast domain
user domain
27. As the network administrator you have been asked to implement EtherChannel on the corporate network. What does this configuration consist of?
providing redundant links that dynamically block or forward traffic
grouping multiple physical ports to increase bandwidth between two switches*
grouping two devices to share a virtual IP address
providing redundant devices to allow traffic to flow in the event of device failure
28. Which characteristic would most influence a network design engineer to select a multilayer switch over a Layer 2 switch?
ability to build a routing table*
ability to aggregate multiple ports for maximum data throughput
ability to provide power to directly-attached devices and the switch itself
ability to have multiple forwarding paths through the switched network based on VLAN number(s)
29. A network administrator is planning to add a new switch to the network. What should the network administrator do to ensure the new switch exchanges VTP information with the other switches in the VTP domain?
Configure the correct VTP domain name and password on the new switch.*
Associate all ports of the new switch to a VLAN that is not VLAN 1.
Configure the VLANs on the new switch.
Configure all ports on the new switch to access mode.
30. Refer to the exhibit.
Switch SW-A is to be used as a temporary replacement for another switch in the VTP Student domain. What two pieces of information are indicated from the exhibited output? (Choose two.)
The other switches in the domain can be running either VTP version 1 or 2.
There is a risk that the switch may cause incorrect VLAN information to be sent through the domain.*
VTP will block frame forwarding on at least one redundant trunk port that is configured on this switch.
VLAN configuration changes made on this switch will be sent to other devices in the VTP domain.
This switch will update its VLAN configuration when VLAN changes are made on a VTP server in the same domain.*
31. Refer to the exhibit.
The network administrator configures both switches as displayed. However, host C is unable to ping host D and host E is unable to ping host F. What action should the administrator take to enable this communication?
Include a router in the topology.
Associate hosts A and B with VLAN 10 instead of VLAN 1.
Remove the native VLAN from the trunk.
Configure either trunk port in the dynamic desirable mode.*
Add the switchport nonegotiate command to the configuration of SW2.
32. What eliminates switching loops?
hold-down timers
poison reverse
Spanning Tree Protocol*
Time to Live
VTP
33. Refer to the exhibit.
Which switch will be elected the root bridge and which switch will place a port in blocking mode? (Choose two.)
SW1 will become the root bridge.
SW2 will become the root bridge.
SW2 will get a port blocked.
SW4 will get a port blocked.*
SW3 will become the root bridge.*
SW4 will become the root bridge.
34. Refer to the exhibit.
A network administrator has configured OFPF in the topology as shown. What is the preferred path to get from the LAN network that is connected to R1 to the LAN network that is connected to R7?
R1-R3-R4-R5-R6-R7*
R1-R3-R2-R6-R7
R1-R2-R6-R7
R1-R4-R5-R6-R7
35. Which statement describes the autonomous system number used in EIGRP configuration on a Cisco router?
It carries the geographical information of the organization.
It functions as a process ID in the operation of the router.*
It is a globally unique autonomous system number that is assigned by IANA.
It identifies the ISP that provides the connection to network of the organization.
36. An EIGRP router loses the route to a network. Its topology table contains two feasible successors to the same network. What action will the router take?
The DUAL algorithm is recomputed to find an alternate route.
The router uses the default route.
The best alternative backup route is immediately inserted into the routing table.*
The router will query neighbors for an alternate route.
37. What is a function of OSPF hello packets?
to send specifically requested link-state records
to discover neighbors and build adjacencies between them*
to ensure database synchronization between routers
to request specific link-state records from neighbor routers
38. Refer to the exhibit.
R1 and R2 are OSPFv3 neighbors. Which address would R1 use as the next hop for packets that are destined for the Internet?
FF02::5
2001:DB8:ACAD:1::2
2001:DB8:C5C0:1::2
FE80::21E:BEFF:FEF4:5538*
39. Match the description to the term. (Not all options are used.)
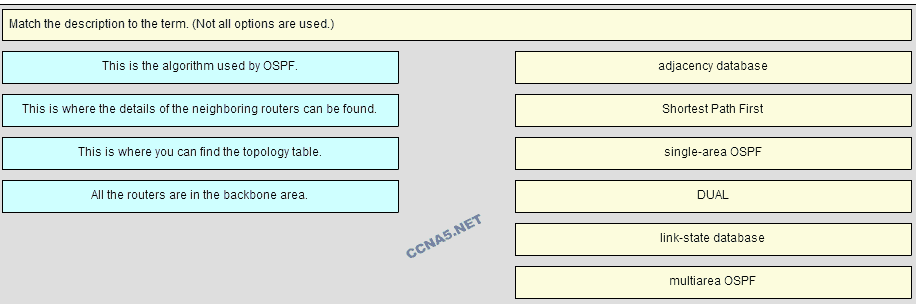
Place the options in the following order:
This is where the details of the neighboring routers can be found. -> adjacency database
This is the algorithm used by OSPF. -> Shortest Path First
All the routers are in the backbone area. -> Single-area OSPF
– not scored –
This is where you can find the topology table. -> link-state database
– not scored –
40. Match the order of precedence to the process logic that an OSPFv3 network router goes through in choosing a router ID. (Not all options are used.)





